what is permeability test of soil|permeability of soils chart : purchaser The objective of constant head permeability test is to determine the coefficient of permeability of a soil. Coefficient of permeability helps in solving issues related to: Yield of water bearing strata. Stability of earthen dams. . 8 de dez. de 2023 · Frio fora de época vai marcar o começo do sábado em grande número de cidades do Sul do Brasil com temperatura abaixo da média de dezembro. O sábado vai começar com temperatura baixa para esta época do ano em muitas cidades do Sul do Brasil, em particular do Rio Grande do Sul e de Santa Catarina. As mínimas cairão a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBNobreak SMS PREMIUM 1500 VA. 1500 VA. Comparar. Novo. Nobreak SMS GAMER 1500 VA. 1500 VA. Comparar. Página 1 de 6. Ampla gama de Nobreaks para diversas aplicações e necessidades.
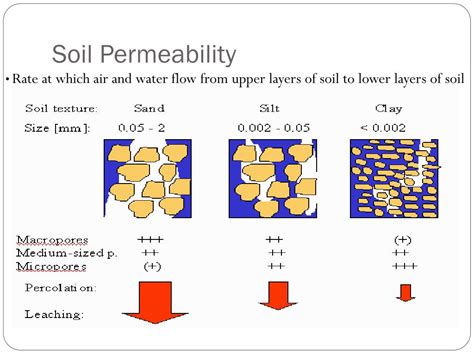
Permeability, as the name implies (ability to permeate), is a measure of how easily a fluid can flow through a porous medium. In geotechnical engineering, the porous medium is soils and . The permeability of a soil is the capacity of the soil to allow water to pass through it. Soil permeability is usually represented by the . What is Soil Permeability? Soil permeability is a measurement dictating how quickly water can pass through a soil sample. We use permeability testing to assess how effectively soil allows water to travel through it. In . Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter .
The objective of constant head permeability test is to determine the coefficient of permeability of a soil. Coefficient of permeability helps in solving issues related to: Yield of water bearing strata. Stability of earthen dams. .
Variable Head or Falling Head Permeability Test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed time interval. Constant head method is suitable for coarse grained soils which are relatively more . Soil permeability testing. This technique reveals the hidden features of soil, offering special soil testing information about water flow and retention which are important for effective soil management. TL;DR. We aim .
Overview of Laboratory Methods Testing Soil Permeability. The most accurate permeability measurement technique involves laboratory constant head testing per ASTM D2434 standards using specialty columnar chambers allowing . The advantages of utilizing laboratory equipment for soil permeability testing include ease of control and sample preparation, the ability to control compressive stress, and the convenience of specimens with .
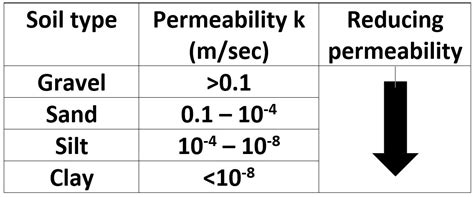
typical permeability values of soil
Soil compaction due to construction activities and increased foot traffic, the presence of impervious surfaces like roads and buildings, soil sealing, altered soil composition, drainage systems, and pollution all contribute to reduced soil permeability in urban areas (Fig. 8.1). This decreased permeability leads to increased surface runoff . Falling Head Permeability Test. This is also known as the Variable head permeability test. The head-causing flow in this method is not as constant as in the previous method. The falling head permeability test is employed for the permeability of soil like fine-grained soil, and clay. Fig.2. Falling Head PermeameterInfiltration and percolation are two concepts that describe the rate at which water moves into the soil (infiltration) and through the soil profile, vertically and horizontally (percolation). And permeability explains how well water can move through the porous media or the soil. Water movement in soil video:
What is Soil Permeability? Soil permeability is a measurement dictating how quickly water can pass through a soil sample. We use permeability testing to assess how effectively soil allows water to travel through it. In general, water travels quickly through highly permeable soils and slowly through soils with low permeability.
The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils. A separate constant head method for granular soils has been recommended by Indian Standards (IS: 2720 – Part 36, 1975).
PERMEABILITY General Most rock and soil contains numerous open spaces where water may be stored and through which water can move. Permeability, or hydraulic conductivity, is a measure of . Permeability Test Method 1 for consolidated material is used only within the vadose zone and is the preferredThe permeability test is the measure of the flow of a liquid through a soil sample. A soil consists of solid particles with void spaces in between. Generally a granular material (sands & gavels) has larger void spaces allowing higher flow, and a fine grained soil .Capillarity-Permeability Test: The set-up for the test essentially consists of a transparent tube about 40 mm in diameter and 0.35 m to 0.5 m long in which dry soil sample is placed at desired density and water is allowed to flow from one end under a constant head, and the other end is exposed to atmosphere through air vent.This lab exercise focuses on understanding soil permeability, which is the ease with which air, water, and roots penetrate through the soil. The experiment involves using plastic pots lled with various samples of sand or soil and measuring the . Testing the permeability of gravel; coarse, medium, and ne sand; and soil. Retention .
4. Testing Procedure for Permeability in a Triaxial cell using Clisp Studio. This test refers to the Constant head permeability method. At the time of writing, VJ Tech complies to BS1377-6:1990, EN ISO 17892-11 and D5484-16 (Method A). a. Sample Preparation. The preparation of the soil specimen should be made according to the testing standard.Permeability is a property of a porous medium like soil by virtue of which any fluids are able to flow through that medium. Permeability of soil can be found either in a lab or in field conditions. Important methods of permeability testing, used in both lab .Permeability is a property of porous materials that is an indication of the ability for fluids (gas or liquid) to flow through them. Fluids can more easily flow through a material with high permeability than one with low permeability. [1] The permeability of a medium is related to the porosity, but also to the shapes of the pores in the medium and their level of connectedness. [2] A good knowledge of soil permeability is needed for estimating the quantity of seepage under dams and dewatering to facilitate underground construction. Soil permeability, also termed hydraulic conductivity, is measured using several methods that include constant and falling head laboratory tests on intact or reconstituted specimens .
Soil consolidation refers to the process by which the volume of a partially or fully saturated soil decreases due to an applied stress. When a load is applied to a low permeability soil, it is initially carried by the water that exists in the .Permeability Test: This test assesses the soil’s ability to transmit water. The most common methods are the constant head permeability test and the falling head permeability test. Shear Strength Tests: These tests evaluate a soil’s .Soil acts as a sponge to take up and retain water. Movement of water into soil is called infiltration, and the downward movement of water within the soil is called percolation, permeability or hydraulic conductivity. Pore space in soil is the conduit that allows water to infiltrate and percolate.A permeability coefficient is most commonly determined through the use of two main laboratory tests: the constant head permeability test and the falling head permeability test. For highly granular soils such as sands and gravels, the constant head method is best and can yield accurate results even if the sample has been disturbed or reconstituted.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the coefficient of permeability by a constant-head method for the laminar flow of water through granular soils. The procedure is to establish representative values of the coefficient of permeability of granular soils that may occur in natural deposits as placed in embankments, or when used as base courses under pavements.
🕑 Reading time: 1 minute A soil is said to be permeable when it allows water through it. There are various factors such as void ratio, size, and shape of the particle, degree of saturation os soil etc. which are affecting permeability property of soils and these factors are briefly discussed in this article. Before going to know about these factors, take a look at the general expression for .
Soil permeability, also termed hydraulic conductivity, is measured using several methods that include constant and falling head laboratory tests on intact or reconstituted specimens .DEFINITION OF PERMEABILITY Permeability is a measure of a given porous medium ability to permit fluid flow through its voids. Any material with voids is Porous and if the voids are interconnected, possesses permeability. Therefore, rock, concrete, soil, and many engineering materials are both POROUS and PERMEABLE. However, among themVariable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow water to flow its pores or voids.
Soil compaction affects various properties, including: Soil Structure: Soil compacted below the O.M.C typically exhibits a flocculated structure, while compaction above the O.M.C results in a dispersed structure. Permeability: Soil permeability decreases with increasing water content on the dry side of the O.M.C due to changes in void sizes. Soil Permeability Tests. Soil permeability is typically obtained from samples taken to the laboratory. There are two types of laboratory test: Falling Head Test and Constant Head Test. Standard test protocols are available, such as ISO. 17892-11:2019. Falling Head Test
Procedure for the Falling Head Soil Permeability Test. The falling head soil permeability test works like the constant head test. The difference is that the water head will not be constant but will decrease/fall with time. The step-by-step procedures for the falling head permeability test are as follows:
how to test external hard drive health
how to test external hard drive speed
webPremium seating area as part of the Pinnacle Club Level. Full FedEx Forum Seating Guide. Rows in Section P13 are labeled A-K. An entrance to this section is located at Row K. have 8 seats labeled 1-8. has 9 seats labeled 1-9. has 10 seats labeled 1-10. When looking towards the court/stage, lower number seats are on the right.
what is permeability test of soil|permeability of soils chart